
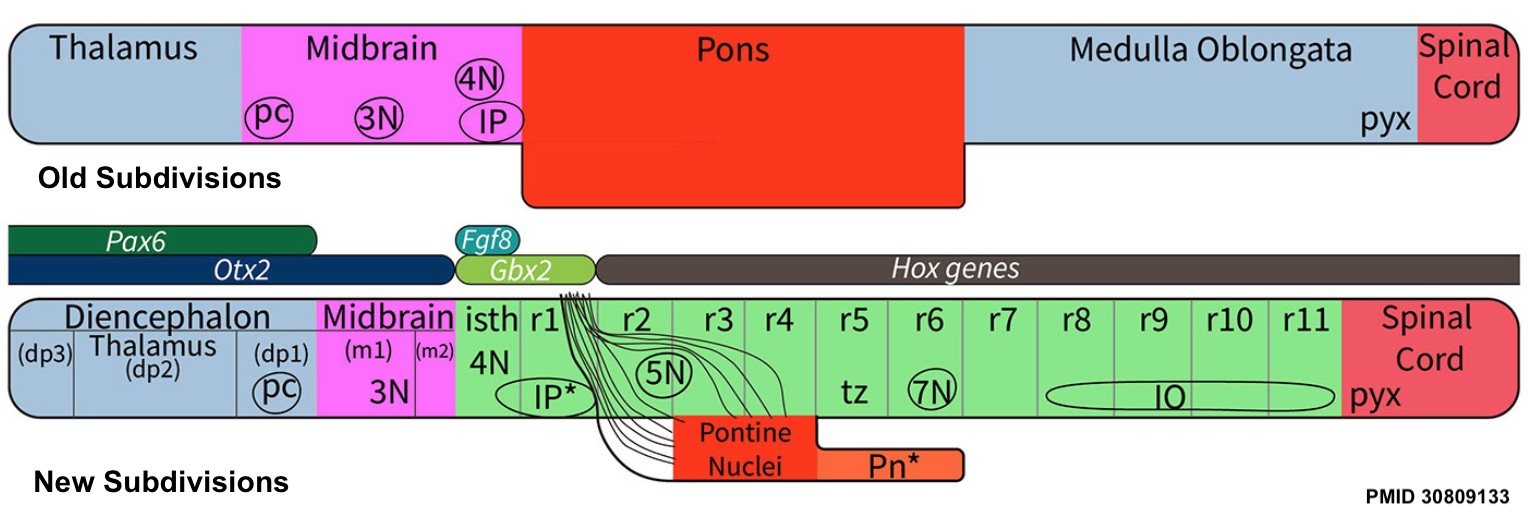
Most brain stem tumors develop in the pons and grow in a part of the brain stem where it can be difficult to perform surgery, making brain stem glioma challenging to treat (see the Types of Treatment section).īrain stem glioma occurs most commonly in children between the ages of 5 and 10 years old. A focal tumor is often less likely to grow and spread quickly. A small percentage of brain stem tumors are very localized, called focal tumors.
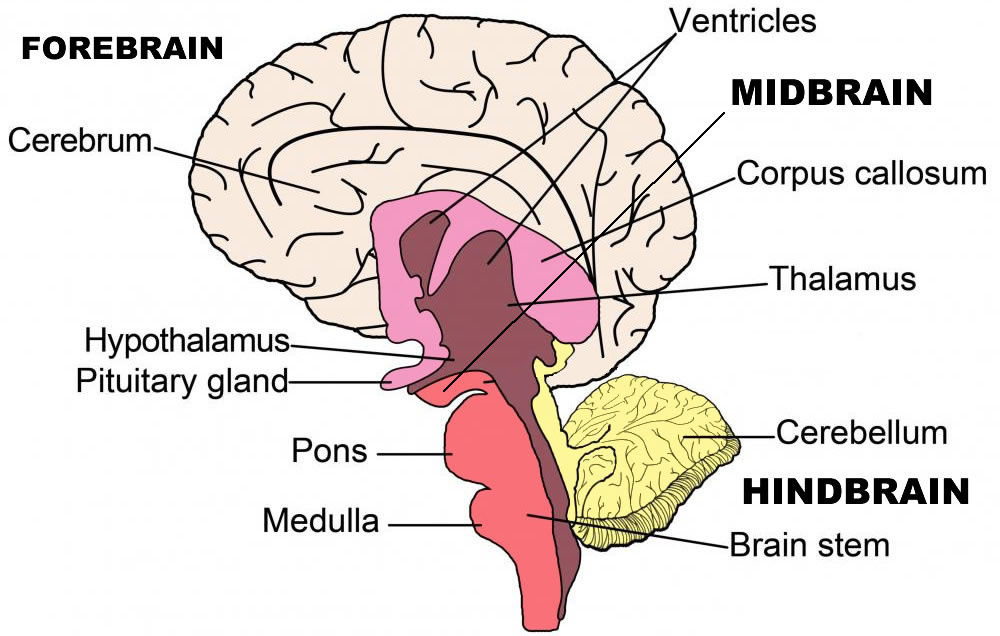
This type of tumor is typically very aggressive, meaning that it grows and spreads quickly. This means it has spread freely through the brain stem. Usually, by the time brain stem glioma is diagnosed, it is most often diffuse. A glioma is a tumor that grows from a glial cell, which is a supportive cell in the brain. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. This type of tumor begins when healthy cells in the brain stem change and grow out of control, forming a mass called a tumor. The pons, which is located between the medulla oblongata and the midbrainīrain stem glioma is a type of central nervous system (CNS brain and spinal cord) tumor. The medulla oblongata, which connects to the spinal cord primary function is to integrate motor, sensory, and cognitive performances between the cerebral cortex on one side of the brain to the same region on the other side. The midbrain, which develops from the middle of the brain It controls many of the body’s basic functions, such as motor skills, sensory activity, coordination and walking, the beating of the heart, and breathing. The brain stem is the lowest portion of the brain, located above the back of the neck. The brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord. Think of that menu as a roadmap for this entire guide. This is the first page of Cancer.Net’s Guide to Childhood Brain Stem Glioma. Superior temporal gyrus – ridge located inferior to lateral sulcus, responsible for the reception and processing of sound.ON THIS PAGE: You will find some basic information about childhood brain stem glioma and the parts of the body it may affect. Postcentral gyrus – ridge directly posterior to central sulcus, location of primary somatosensory cortex. Precentral gyrus – ridge directly anterior to central sulcus, location of primary motor cortex. Lunate sulcus – groove located in the occipital cortex. Lateral sulcus – groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. Central sulcus – groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes. The brainstem contains both white and gray matter. The two cerebral hemispheres are connected by a white matter structure, called the corpus callosum. It serves as the connection between the cerebral hemispheres with the medulla and the cerebellum and is responsible for basic vital functions, such as breathing, heartbeat blood pressure, control of consciousness, and sleep. Mater) descends vertically to fill this fissure.

There is a substantial amount of evidence that the brainstem plays an integral role in regulating consciousness and awareness. The brain stem handles the most basic functions required for survival things like, heart rate, reflexes, breathing, digestion, and regulating sleep.

It isĭivided into two anatomically symmetrical hemispheres by the longitudinal fissure – a major sulcus that runs in the median sagittal plane. The brain stem is the lowest and oldest region of the brain. Externally, the cerebrum has a highly convoluted appearance, consisting of sulci (grooves or depressions) and gyri (ridges or elevations).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
